The value of pi(π) through geometry
The Discovery of pi is a breakthrough in the evaluation of mathematics. Calculation of its value is a very big task, as pi is an irrational number so we cant write it as a fraction but we use 22/7 which is an approximate value of pi.
Now we will be going to discuss how we can verify the value through some simple geometrical simulation here we will see a simple simulation in Geogebra.
We know that,
pi=periphery/diameter
We can measure diameter easily, the accuracy of pi will depend on the accuracy of measurement of the periphery. For this, if we assume a circle made up of polygon then if the number of side in polygon tends to infinite then, “(sum of their side)/diameter” will tend to pi.


Here when we take polygon with four side value of (sum of their side)/diameter is not accurate but as we increase the number of sides it starts shifting towards pi.

Now we can see that when we take the number of side to 28, it become 3.14 which correct up to two-digit.
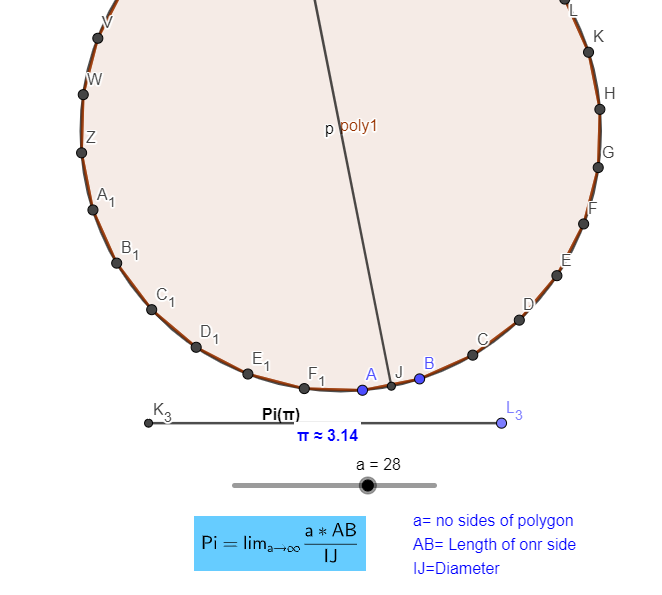
Hence like this, we can calculate the value of pi by just increasing the number of sides.
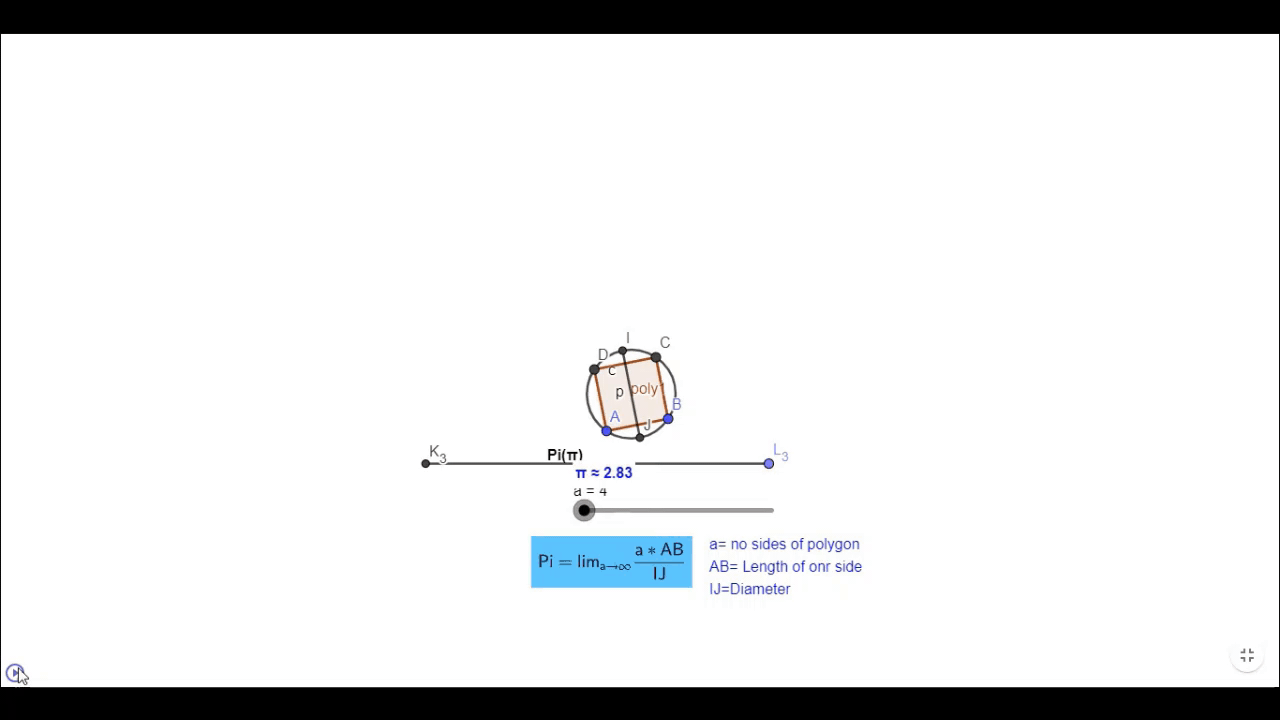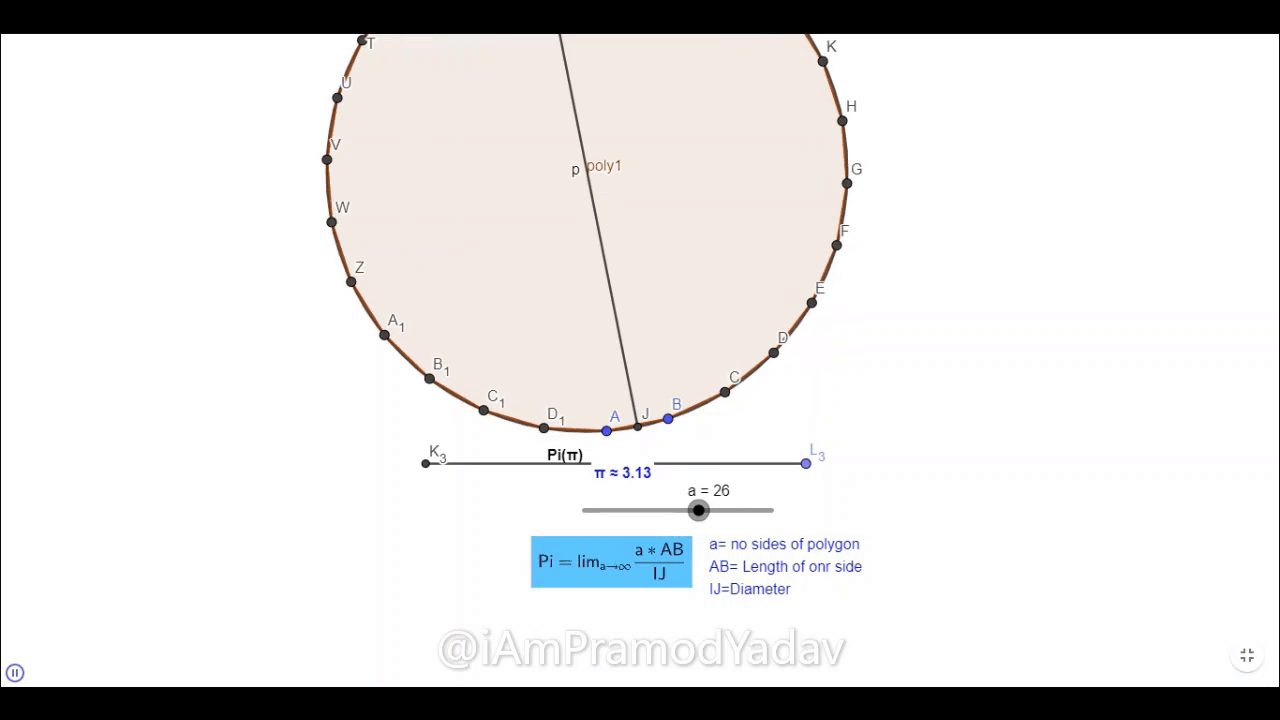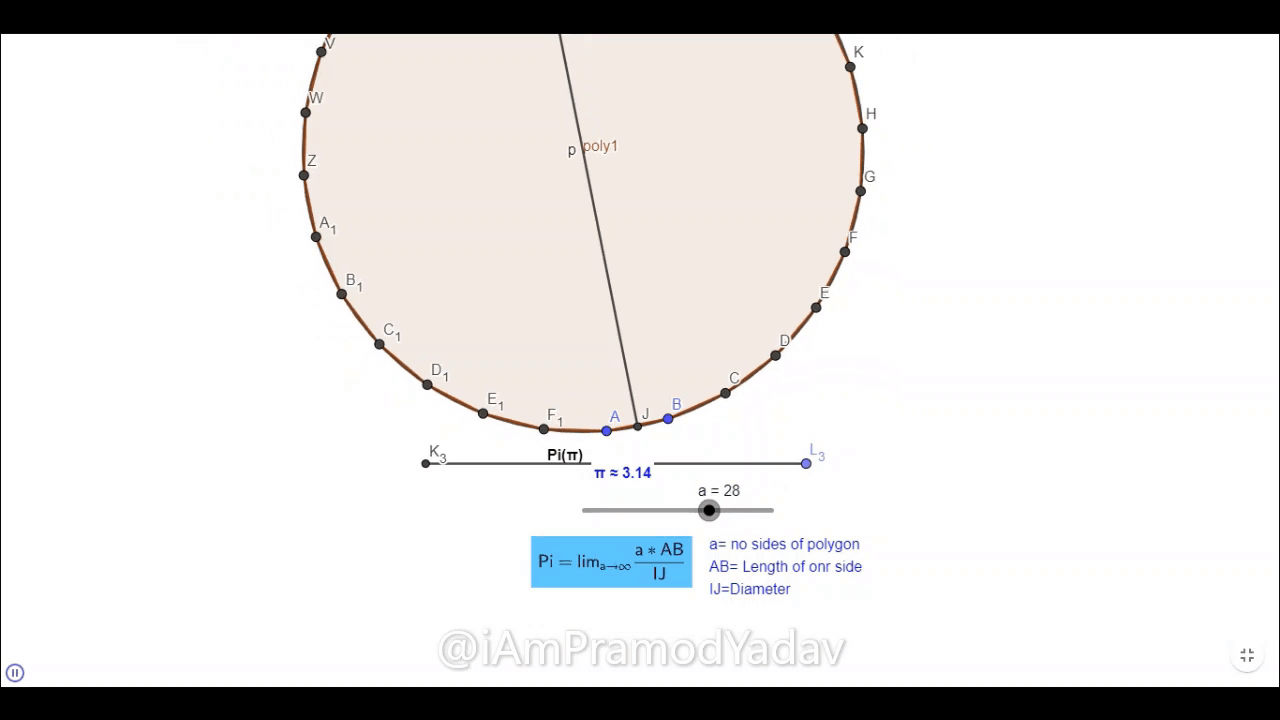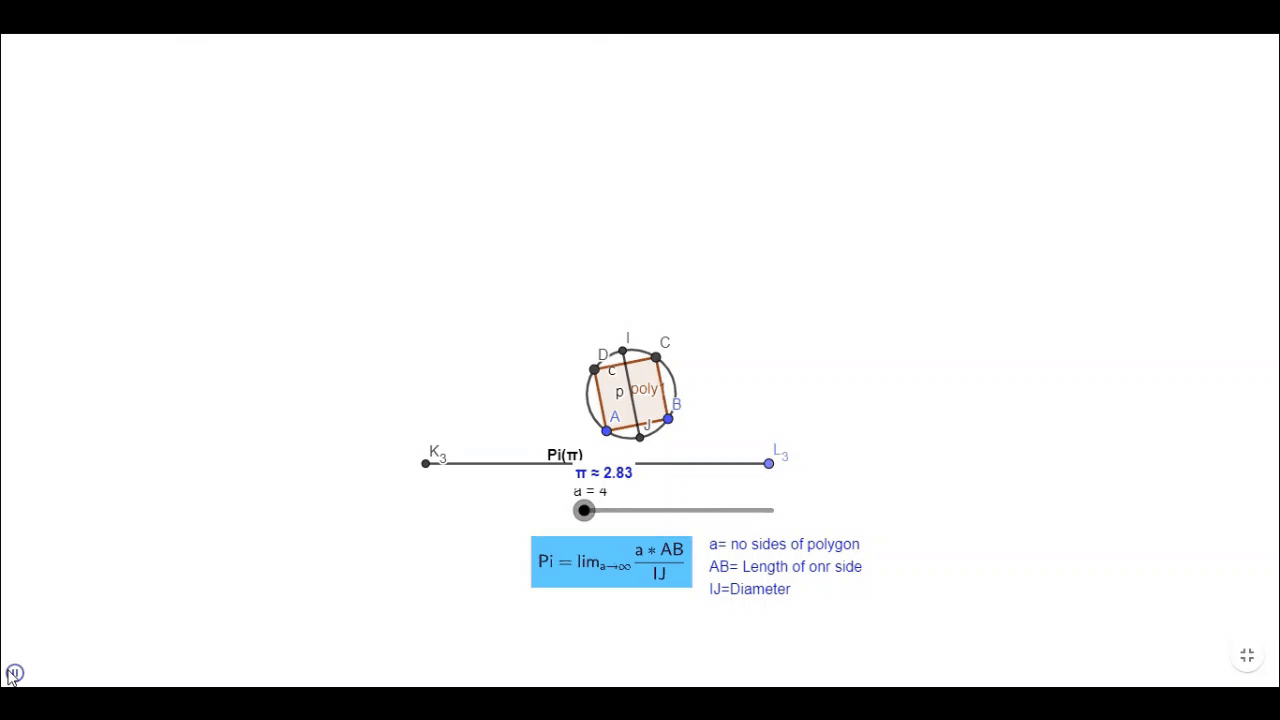
This simulation is made in Geogebra Classic. you can play with it with this link https://www.geogebra.org/m/pdwbycbn.
Thanks for reading.
